This blog is for users of the Microsoft Windows Operating System, it contains tips, tricks and secrets for both beginner and expert users.
Tuesday, October 31, 2006
Windows Media Player 11 Hits the Street
Windows Media Player 11 is finally here. It has a slick new interface and lots of new features. Read the article to get a quick run down of some of the new functionality.
The player is available for download here.
Monday, October 30, 2006
Free and Low Cost Office Suites (and other stuff)
There are several options available to you. Some of these suites require that they be install on your local computer, and others can be run from within your browser.
Personally I am a big fan of Microsoft Office, and I have a hard time using anything less. The one problem with Office is that its not free or low cost.
If you just have basic word processing needs, such as writing letters to your friends and family, or creating simple spreadsheets or presentations. Then Microsoft Office might be over kill for you, there several other choices available that might be a better fit for your needs.
Out of all the free, low cost, or online office suites available, OpenOffice.org is the best IMHO. Then after that I would start to look at everything else and see what fits your needs. Whatever you look at, make sure its has the features that you're going to use.
All these tools are pretty good for doing basic things like creating a document, managing numbers, etc. Although, for tasks that are more complicated, you're going to need a real office suite like OpenOffice.org or Microsoft Office.
Office Suites
Browser Based:
- ThinkFree: A Java-based browser office suite. Includes word processor, presentation and spreadsheet application.
- Google Docs & Spreadsheets: An AJAX-based browser office suite. Includes a word processor and spreadsheet application.
- ZOHO: An AJAX-based browser office suite. Includes a word processor, presentation spreadsheet application, and more.
- OpenOffice.org: One of the best office suites available. Includes a word processor, presentation and spreadsheet application.
- AbiWord: A free word processor application.
- Dia: An open source vector graphic program.
- GIMP: An open source bit-map drawing program.
- Scribus: An open source page layout program.
- Meebo: A browser based universal instant messaging client. Supports: AIM, ICQ, MSN Messenger, Yahoo Messenger, Jabber and GTalk.
- Trillian: If you have multiple accounts across several IM services this is a great IM client. Supports: AIM, ICQ, MSN Messenger, Yahoo Messenger, and IRC.
Browser Based:
- Gmail/Google Calendar: Provides: e-mail, calendaring, contacts and notes.
- Yahoo! Mail: Provides: e-mail, calendaring, contacts and notes.
- Contact Office: Provides: email, calendaring, address book, fax, SMS, phone calls, etc.
- Thunderbird: An e-mail client, with spam filtering.
- Sunbird: Calendaring with a task manager.
Below are some extra resources that you may need in your day-to-day activities.
Software:
- GnuCash: Personal and small-business financial-accounting software.
- Free Templates: Free label templates for: Avery, CDs, address, mailing, shipping, etc.
- 1001 Free Fonts: Thousands of free fonts are available for download.
- Answer.com: Need information about a word or subject, this site includes dictionary, thesaurus, encyclopedia (uses Wikipedia), and more.
- Currency Converter: Lookup current exchange rates for just about any currency.
- Martindale's Reference Desk: A great collection of links to different types of references available on the web.
- Martindale's On-Line Calculators: A great collection of links to different types of calculators available on the web.
- RefDesk: A great collection of reference resources that are available on the Web.
- Unit Converter: Convert just about any numerical data from one unit type to another.
- World Clock: A web-based world time clock.
- Yearly Calendar: A web-based yearly calendar.
Saturday, October 28, 2006
Network: Error Message - "Network Cable Unplugged"
Until the day they get a message that says 'Network Cable Unplugged.' It sounds simple and could be but this same message could also mean something more then the cable is unplugged. This same message could mean that you have a short in your cable, your network card has stopped functioning, etc.
Follow the steps below to help diagnose this problem:
- Verify the cable is plugged in at both ends, press it in see if you hear a click. Check your computer and see if the message goes away. If it doesn't unplug the cable at both ends, then plug it back in.
- If this is a new cable, make sure that its not a crossover cable (check the bag that it came in) you need a straight through network cable. Also some network switches have an uplink port or a button to make a port an uplink port. If the uplink button is enabled disable it, this is only needed if you're hooking two switches together without a crossover cable.
- When the cable is plugged in you should see a green light (or even a flashing green or amber light) on the switch and on your computer. If you're not getting these lights after you check the cable in the previous step, try changing out the cable.
- If you're not getting any lights on your network switch, make sure its plugged in and getting power. Most switches have some type of diagnostic lights, if you don't see them the wall plug, power transformer, or network switch could be bad.
- If you know your switch is working, try plugging the cable into a different port on it. Its not to uncommon for a port to go bad on the network switch or an Ethernet card. If you have another computer that you can plug the cable into try that. If you know the port is working on the network switch, try using a different Ethernet card in your computer.
- Before you switch out the Ethernet card in your computer, check to see if you can find it in your Windows Device Manager. If you do see it you can try to uninstall and reinstall it again (this will require that you already have the driver for this device on your computer). If you don't see your network card in the Device Manager try downloading the driver from the manufacture's web site.
Wednesday, October 25, 2006
Software: Microsoft Windows Defender Released
So far, I have not been infected by any virus or spyware, but I can't give all the credit to the scanner. I avoid downloading stuff from the Web that I shouldn't, that is the best way to prevent getting any type of malware.
Below is a list of some of the new features of the scanner:
- Enhanced performance in the new scanning engine.
- A simplified user interface and alerts.
- Globalization and localization features, with multiple language support.
- Support for Microsoft Windows XP Professional x64 Edition.
- Automatic cleaning according to your settings during regularly scheduled scans.
Tuesday, October 24, 2006
Article: Firefox 2.0 Scheduled For Release on Tuesday
I have been playing with the release candidate of this browser for a few weeks now. It has some nice new features, but their not revolutionary.
I have one major complaint about this version of Firefox, several of my favorite extensions stopped working. So be prepared to be disappointed here.
Personally, I believe that the ideas for most of the new features in the browser were borrowed from the more popular extensions. Below is a list of some of the new features:
- Phishing filter warns you when you're visiting a fake web site.
- A new search feature that displays suggestions as you type your search request.
- A session manager that restores the windows and tabs you had opened before a crash.
- A spelling checker that spell checks your input into web forms.
- Better RSS support.
Monday, October 23, 2006
Wireless: Optimizing and Troubleshooting a Wireless Network Connection
it adds an entry for that network in to the 'Preferred Network' list. This list is meant to remember your network settings when you move from wireless network to network. The problem is that if you move between a lot of different wireless networks this list can get really filled up with a lot of junk that can slowdown your network connection time.
Another problem that happens often is that you can find yourself constantly being connected to a wireless network that you don't want to be connected to. This problem is caused by the fact that the entry for the wireless network that you don't want to be connected has a higher order of preference then your preferred network.
To fix both of these problems:
- From the Control Panel folder, open the Network Connection folder.
- Right click on the Wireless Network Connection icon, and select Properties
- Click the Wireless Networks tab.
- In the 'Preferred Networks' list, highlight and delete any wireless networks that you don't use. If there is a network that you use more often then others. Highlight the network and press the 'Move Up' button to move it to the top of the list.
- Press the OK button when don't
Thursday, October 19, 2006
Windows XP: Internet Explorer 7 is now available...
Some of the new improvements in the browser include: security protection, a redesigned user interface, and a development platform. Below is a high level list of the major new features:
- Phishing Filter (reports if a web site is not who it really is)
- RSS Reader (allows you to read RSS feeds in the browser)
- Tabbed browsing (open multiple web pages in a single window)
- Toolbar search box (quickly search from the toolbar)
- Advanced printing (optimized web page printing)
- Security Status Bar (displays different colors in the status bar to notify you how safe the web site might be)
- Privacy Cleaner (quickly deletes your browser cache, cookies, and other data that might contain personal information)
- And more...
Wednesday, October 18, 2006
Security: Rootkits Tools
There are several types of malware (viruses, Trojan horses, rootkits, etc.) that are in the wild on the Internet. Some types of malware will find and infect you if you're not running a firewall, others will disguise themselves in the form of an attachment. You can even get infected by visiting the wrong web site if your browser is vulnerable.
Rootkits are the type of malware that doesn't take no for an answer, they will try to exploit every trick they can to get administrator access to your computer. Then once they become an administrator they will deploy their payload.
Most anti-virus and anti-spyware scanners don't properly find rootkits, because they're generally very difficult to detect. Below are some anti-rootkit tools (some free, and others are fee based) that you can run to see if your system is infected by this type of malware.
- Sysinternals: RootkitRevealer (free) - I have talked about this scanner before in a previous article. Although its still a good tool for detecting this type of malware, but it can't remove it.
- F-Secure: BlackLight (free trial until 1/2007) - This application seeks out and tries to remove any rootkits it finds installed on your computer.
- Sophos: Anti-Rootkit (free) - I have talked about this scanner before in a previous article. This application seeks out and tries to remove any rootkits it finds installed on your computer.
Windows XP: Automate the Disk Cleanup Tool
Now, I am going to show you how to automate this process. Its relatively easy to do, all you have to do is follow the instructions below:
Configuring the Disk Cleanup tool:
- From the Run... command, type "cleanmgr /sageset:1" and press the OK button.
- You can have up to 0 - 65535 profiles, all you have to do is change the number after '/sageset'. Make sure you remember the number you selected for the profile you will need it for the next section.
- When the Disk Cleanup dialog displays, select or unselect the type of files that you want to remove when the tool is run.
- Press the OK button.
- From the Run... command, type "cleanmgr /sagerun:1" and press the OK button.
- Make sure to use the session number (i.e.: 1 in the example above) for the Disk Cleanup profile you created in the previous section.
The 'cleanmgr /sagerun:1' command can be run from the MS-DOS prompt, added to a script, or run from the 'Scheduled Tasks' feature on a regular basis.
Tuesday, October 17, 2006
Software: Changing the World with Your Screen Saver
The screen saver utilizes the unused processing power of your computer, as a part of a large distributed computing cluster. These clusters can be composed of thousands (or more) of computers working together for a common goal. The way these large clusters work is each computer downloads a small part of a larger problem, and computes the data and sends the results back to the master computer.
Below is a list of some of the projects that are available:
- boinc.berkeley.edu: Stands for 'Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing', here is a brief list of some of the current projects: Climateprediction.net, Seasonal Attribution Project, BBC Climate Change Experiment.
- folding.stanford.edu: Searches for treatments for Alzheimer's, Huntington's, and other related diseases.
- grid.org: Searches for treatments for cancers, and other diseases.
- SETI@home: Analyze radio telescope data in the search for extraterrestrial life.
- www.worldcommunitygrid.org: Searches for treatments for cancers, and other diseases.
Thursday, October 12, 2006
Windows XP: Disabling Services and Devices Based on Hardware Profile
To disable services based on a hardware profiles:
- From the 'Administrative Tools' folder, double-click on Services.
- Double-click the service you want to modify
- Click the Log On tab in the properties dialog
- Click disable for the selected Hardware Profile.
- Open the 'Device Manager'
- Double-click the device you want to modify.
- In the General tab under the 'Device Usage' label select 'Do not use this device (disable)' option
- Press the OK button.
Wednesday, October 11, 2006
Windows XP: Recovering from a Failed Driver Installation
- Uninstall the device driver, restart the computer and try reinstalling it again.
- Try using the Driver Roll Back feature.
- Try using the System Restore feature.
- From the Start menu > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > System Restore. Follow the instructions in the wizard.
- Reboot the computer, press F8 at startup, and select 'Last Known Good Configuration' and press the Enter key.
- From the MS-DOS prompt, type "sfc.exe /scannow" (this runs the System File Checker). It verify the protected system files, and if problems are found it will revert them to a previous version.
Tuesday, October 10, 2006
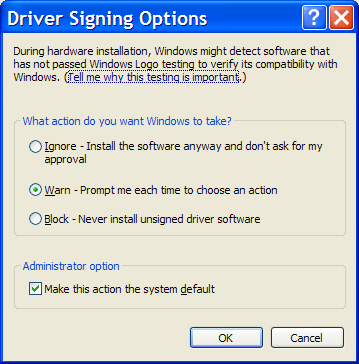
Windows XP: Driver Signing
Drivers can come from many different sources, like an installation CD, a web site, or other various sources. Some device drivers are not digitally signed by Microsoft, which could mean that they may not have been tested as thoroughly as they could have been. There's a greater chance that they could effect the stability of your system because of unknown compatibility issues.
To configure how these signed and unsigned drivers are handled by the OS, you need to open the 'Driver Signing Options' dialog:
- Open the Control Panel folder.
- Double click the System applet.
- Click the Hardware tab.
- Press the 'Driver Signing' button.
- Ignore (Allows the installation of any files, signed or not.)
- Warn (Displays a warning message that the driver being installed is not signed.) [Default]
- Block (Prevents the installation of unsigned drivers).
Monday, October 09, 2006
Windows XP: Ways to Install New Device Drivers
- Setup Program: This is software that comes with your new device. To install this software, generally requires putting a CD/DVD in your computer or downloading the setup application from the device manufacturer's web site.
- Note: Some devices require that the installation software is installed first before you hook the hardware up to your computer. This is done to make sure the device is properly detected.
- Booting Your Computer: Every time Windows starts it scans the system for new hardware that might have been added or removed since it was last on. After the system is fully booted, if new hardware is detected it will check if the system already has the appropriate driver for it. If not, it will request that you provide the location of the driver it needs.
- New Hardware Scans: Sometimes after you boot Windows, you may not have the right drivers for new hardware that was added at that moment. After you get the right driver, you use the Add Hardware Wizard (select the Add Hardware icon in the control panel) to manually perform the hardware-detection and installation process to install the appropriate device driver.
- Manual Installation: Sometimes device drivers don't come with an installation program, but instead they come with .INF files. You can right-click these files and choose Install to add these new drivers.
Friday, October 06, 2006
Security: Simplifying Web Site Logins
I recently came across a very cool browser-based utility that simplifies using, creating and remembering strong passwords across any web site. All you have to do is create a master password that only you know, and give the site a URL (such as: http://www.google.com), it will then create a unique password for that web site. You can also create a bookmarklet (JavaScript embedded in to a bookmark) that you can store in your browser links bar, that can automatically generate a password for a site that your visiting based on your master password.
The way this utility works is by using JavaScript on a local web page loaded in your browser (no information is sent to the remote server). The script then uses MD5 to create a one-way hash based on your master password and the domain of the web site that you're going to use it for. Only the first eight (or more) characters of the hash are selected, so its impossible to break the hash because not all the information is used.
Thursday, October 05, 2006
Windows XP: Turning Off the Language Bar
- Open the Control Panel folder.
- Double-click 'Regional and Language Options' applet.
- Click the Languages tab.
- Under 'Text services and input languages', press the Details button.
- Under Preferences, press the 'Language Bar' button.
- Uncheck the 'Show the Language bar on the desktop' checkbox.
- Press the OK button twice.
Wednesday, October 04, 2006
Security: Internet Privacy is an Oxymoron
Did you know that there is no such thing as true anonymity or privacy on the Internet? All you can do is mask your identity, and make it difficult for someone to know who you are. Although, in most cases its still possible for someone to track and identify you with enough work.
There is a lot of information about you that is leaked by your own personal Internet activities (such as surfing a web site, posting on forums, etc.). Then your computer and its applications (such as your browser, IM client, etc.) are doing their own fair share to help leak more information.
Anything that contains your name, address, etc. Is known as 'personally-identifiable information' (PII), because it can personally identify you directly. This information is generally provided by you to some web site or service (such as Amazon, eBay, etc.) that you may use regularly.
Any of the information (PII or not) is used to profile how you surf the web, what you buy, and other types of demographic analysis. All most all of this tracking is perfectly legal, and you even grant companies permission to do this when you agree to use a web site through its 'terms of service' or 'privacy policy' that you don't read.
Information Leaked by your Applications
As I said earlier, when you visit a web site there is certain types of information about you that is revealed by your computers applications. A lot of this information (such as your browser cookies) are needed by web-based applications to be able to customize your experience.
Below is a brief list of some of the information a web site can know about you, just by visiting it with a regular browser and Internet connection:
- The type of browser you're using, a long with information about its features. For example: what version of: Java, JavaScript, Flash and other applications you have installed (see: BroswerSpy).
- This doesn't include the information in the HTTP header, which includes information about your browser and the web page you requested from a web site (see the following article for more information).
- There is information in the HTTP header called the 'referer', that also gives the web site your visiting, the last URL of the web site you're coming from. Here is an example, of some of the information a site can see about you.
- Browser cookies and web beacons (an invisible 1x1 graphic on a web page with a unique id embedded in to its name), which can be used identify your computer across different web sites. This technology is generally used by advertising and marketing companies to track and profile your browsing activity to better serve you ads.
- As more web sites become interactive, browser cookies are used to track your web site session information. If you turn off the cookie feature, you can prevent certain web sites from working properly for you.
- Web beacons have been used by spammers to track if you open up an email message, and to see if a email address is valid. Although, most modern email clients prevent images from being downloaded automatically which help prevent information about you from being leaked.
- Your browser keeps local copies of all the web pages you visited in its cache, along with a history of all the URLs you visited. Some browser's like Firefox keep track of the files you downloaded, and the keywords you typed into the search toolbar. Then there is the saved forms information (known as AutoComplete in IE), and saved password feature. This information is used to improve the broswer's user experience, but also can become a privacy issue in some cases.
For example, your instant message client may keep logs of all your conversations. Your e-mail client, keeps all the messages that you received and sent. Your VoIP client keeps a log of all the calls that you make.
Even if you clean all this information off your local computer, your application's service provider has logs and/or copies of it in their servers and databases. Its not uncommon for them to use this information to profile usage habits of their users. All this information is also available to local and federal law enforcement generally with the use of a search warrant.
Generally, no matter what network enabled application your using, the following information is always going to be left about you on some server somewhere.
- Once someone knows your computer's IP address, its possible to isolate the ISP, and therefore the city, state/province, and country your computer's from (see: IP Address Locator).
- Local and federal law enforcement with the use of a search warrant can force the ISP to release your identity, based on your computer's IP address.
- When you visit a web site, information is stored in the web server logs of the time you visited the site, your IP address, which pages you viewed, and sometimes what you searched for on that site (see: Omniture).
- Think about this, all your favorite search engines keep all the information that you searched. If you have a personal account on a site like Google, Yahoo, etc., they can directly tie this information back to you.
- For example: "On August 4, 2006, AOL released three months of search history for 650,000 users to the public. Although the searchers were only identified by a numeric ID, the New York Times discovered the identity of several searchers." (excerpt from the Wikipedia)
- Anytime you visit a web site using it's domain name your computer needs to lookup the IP address of the remote server through some DNS server request. This information is then logged on that computer.
- When you're at work, and you search the Internet your companies web proxies and firewall can track all types of Internet activity. Plus in the U.S.A. any information on your computer, or in your e-mail is property of the company.
With all the data stored on computers these days, a new area of computer criminal science has been created called 'digital forensics'. These are law enforcement personnel specially trained to find and retrieve specific information off a computer.
The tools that these people use are good at extracting the data they want. Generally the programs we use everyday are really good at leaving digital bread crumbs all over your computer's hard drive about everything that you do. These digital forensics tools are designed to leverage this information
On a side note, about digital forensics tools. Did you know that by using a pattern analysis program you can predict if something was written by a man or a women with almost 70% accuracy.
The way this technology works is by analyzing the words used in a message and assigns different values to them to determine if the text was written by a man or women. More information can also be determined by your writing style beside gender, such as your nationality based on the words that you use.
To see this tool in action, check out Gender Guesser or Gender Genie. With technology like this, it means that any of those anonymous posting or e-mail you might have created are becoming a lot less anonymous.
Note: This technology was created by Dr. Neal Krawetz of Hacker Factor Solutions.
Tuesday, October 03, 2006
Article: Firefox Zero-Day Code Execution Hoax?
Monday, October 02, 2006
Windows XP: Accessing the Windows Update Catalog
There can be several reasons why you would want to do this, for example: you have a slow modem at home and you want to get your updates from a faster computer. Or, if you're a systems administrator at a company, and you need to update Windows clients or servers.
Whatever the reason, here is how you can do it.
- Open Internet Explorer (this won't work from Firefox), and go to "http://v4.windowsupdate.microsoft.com/catalog"
- Click the link "Find updates for Microsoft Windows operating systems" or "Find driver updates for hardware devices"
- If you selected the find updates for operating system, you will need to select the OS which you're looking for the updates. Press the Search button to continue.
- Select the category, and then select updates that you want to get.
- Click the "Go to Download Basket" link.
- Press the Browse... button to select the download location on your local computer.
- Press the 'Download Now' button.
- Choose if you want to accept the licensing agreement, then press the appropriate button.